Unlocking Trade Secrets: Calculating Absolute And Comparative Advantage
Absolute Advantage And Comparative Advantage
Keywords searched by users: How do you calculate absolute advantage and comparative advantage Absolute advantage and comparative advantage, how to calculate absolute advantage and comparative advantage, Absolute advantage and comparative advantage example, How to calculate absolute advantage, Absolute advantage là gì, Absolute advantage vs comparative advantage, how to calculate absolute advantage example, Comparative advantage
How To Differentiate Absolute Advantage And Comparative Advantage?
When it comes to distinguishing between absolute advantage and comparative advantage, it’s essential to understand these two economic concepts clearly. Absolute advantage primarily pertains to an entity’s capacity to manufacture a larger quantity of a particular product or provide a specific service compared to others. In contrast, comparative advantage centers on the ability to produce goods and services with a lower opportunity cost when compared to competitors. To elaborate further, absolute advantage concentrates solely on output quantity, whereas comparative advantage takes into account not only output but also the efficiency of resource utilization, making it a more nuanced and comprehensive measure in assessing competitive advantages in trade and production.
What Is Comparative Advantage Formula?
The concept of comparative advantage is a crucial economic principle that helps countries determine their specialization in producing goods and trading them with other nations. It can be calculated using a simple formula:
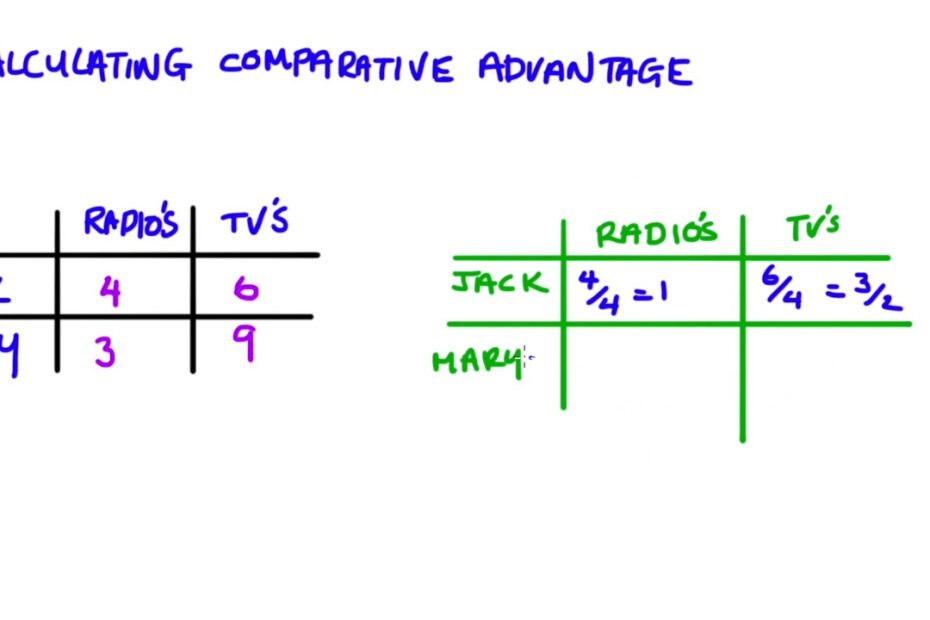
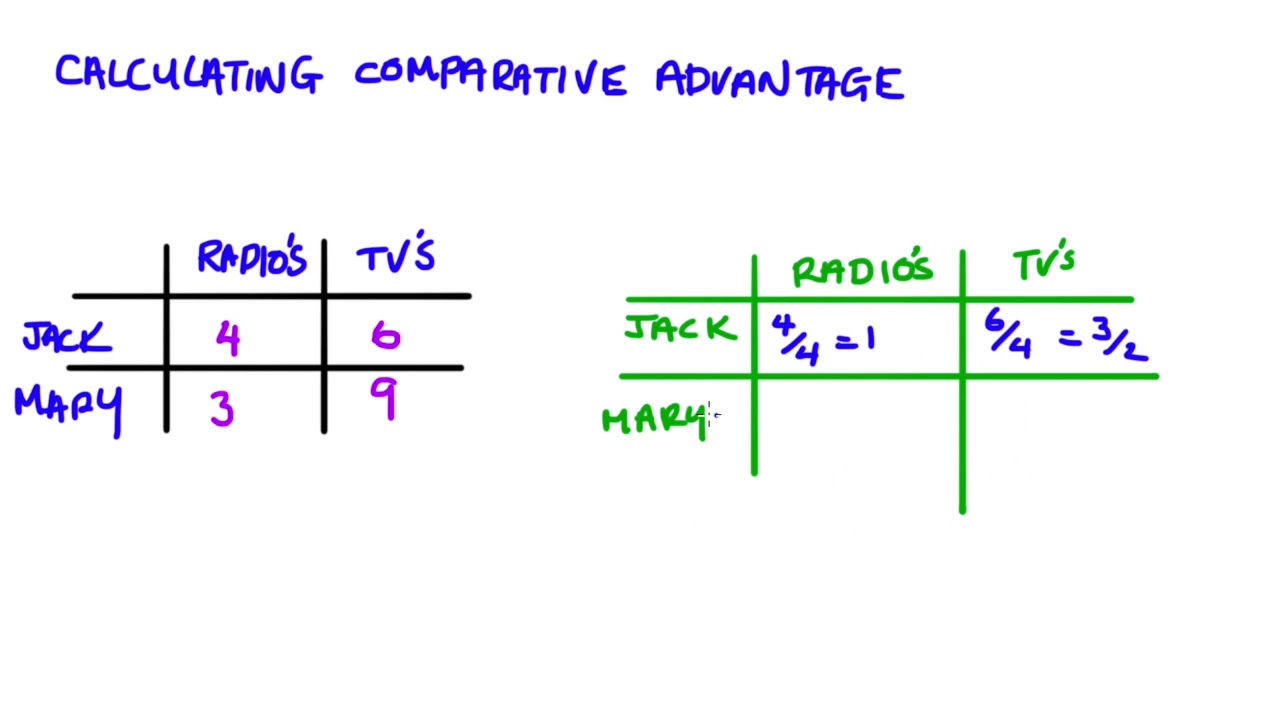
Comparative Advantage = Quantity of Good A Produced by Country X / Quantity of Good B Produced by Country X.
This formula helps countries identify their relative efficiency in producing different goods. By comparing the quantities of two different goods a country can produce, we can determine where its comparative advantage lies. If the result is greater than 1, it implies that the country is more efficient at producing Good A than Good B, indicating a comparative advantage in Good A production. Conversely, if the result is less than 1, the country has a comparative advantage in producing Good B. Understanding comparative advantage is essential for international trade decisions and can lead to mutually beneficial trade relationships between countries.
Can You Have Both Comparative And Absolute Advantage?
Certainly, it is entirely feasible for a country to possess both an absolute and comparative advantage, although this scenario typically pertains to a single specific product. To clarify, a comparative advantage materializes when a nation can manufacture a particular item with a lower opportunity cost compared to both alternative goods within its own economy and the production capabilities of other nations. This dual advantage, where both absolute and comparative advantages coexist, can significantly enhance a country’s competitiveness and economic prosperity. It’s important to note that these advantages are contingent upon the unique factors and resources at play within a specific industry or sector, and they may not extend universally across all goods and services. This concept is crucial for understanding international trade dynamics, as it elucidates how countries can excel in certain areas while still engaging in mutually beneficial trade with others.
Aggregate 21 How do you calculate absolute advantage and comparative advantage




Categories: Update 42 How Do You Calculate Absolute Advantage And Comparative Advantage
See more here: muadacsan3mien.com

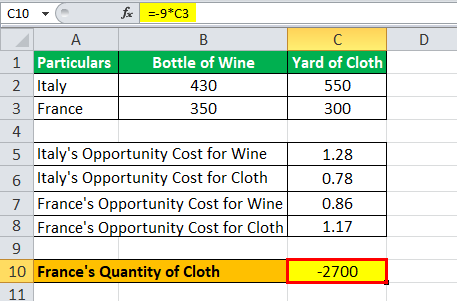
For absolute advantage, we simply need to compare the quantities of output, and the country with the larger quantity wins the absolute advantage. However, comparative advantage is calculated by finding the opportunity cost for each country, and the country with the lower opportunity cost wins the comparative advantage.Comparative advantage is often contrasted with absolute advantage. Where absolute advantage refers to the ability of an entity to produce a greater quantity of a product or service, comparative advantage refers to the ability to produce goods and services at a lower opportunity cost compared to the competition.Comparative advantage is calculated as. Comparative Advantage = Quantity of Good A for Country X / Quantity of Good B for Country X.
Learn more about the topic How do you calculate absolute advantage and comparative advantage.
- Comparative Advantage vs Absolute Advantage – StudySmarter
- Absolute vs. Comparative Advantage: What’s the Difference?
- Comparative Advantage Formula (Calculation, Examples, Explanation)
- Can a country have both absolute and comparative advantage? – Zippia
- Is a Comparative Advantage In Everything Possible for a Country?
- Absolute Advantage Vs. Comparative Advantage: What’s The Difference?
See more: blog https://muadacsan3mien.com/category/space-astronomy