Maximizing Fischer Esterification Yield: Strategies For Completion
Fischer Esterification Reaction Mechanism – Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Keywords searched by users: How can the Fischer esterification be driven to completion Fischer esterification, Esterification Mechanism, fischer esterification procedure, reverse fischer esterification, fischer esterification history, why is esterification reversible, mechanism of ester formation, fischer esterification practice problems
Does Esterification Go To Completion?
Esterification is a chemical process used to create esters, compounds commonly used in various industries. This reaction involves the interaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the presence of a strong acid catalyst. It’s important to note that esterification is a reversible reaction. Additionally, esters can be broken down through a process called hydrolysis, which can be carried out using either an acid or a base. When employing acid hydrolysis, it’s worth mentioning that the reaction is essentially the reverse of esterification. However, it’s important to note that acid hydrolysis doesn’t proceed to completion, meaning not all of the ester will be converted back into its original components.
Why Does Esterification Not Go To Completion?
Why doesn’t esterification reach full conversion? The process of esterification necessitates the presence of a potent acid catalyst, typically sulfuric acid. However, even with this catalyst, esterification remains an equilibrium reaction, meaning it doesn’t reach complete conversion. In cases where the alcohol and carboxylic acid involved have minimal steric hindrance, combining them in a 1:1 ratio will result in an equilibrium mixture containing approximately 70% ester. This equilibrium nature of the reaction arises because, during esterification, the formation of the ester is balanced by the reverse reaction, the hydrolysis of the ester back into the alcohol and carboxylic acid. This equilibrium point prevents the reaction from proceeding to total completion.
Update 9 How can the Fischer esterification be driven to completion
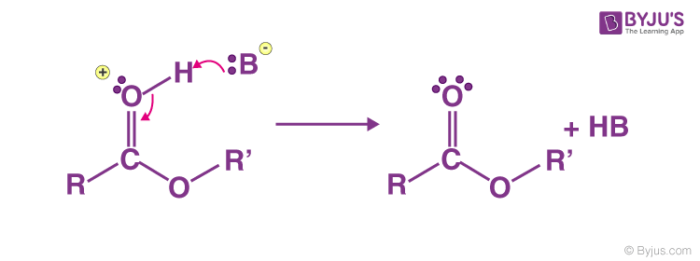

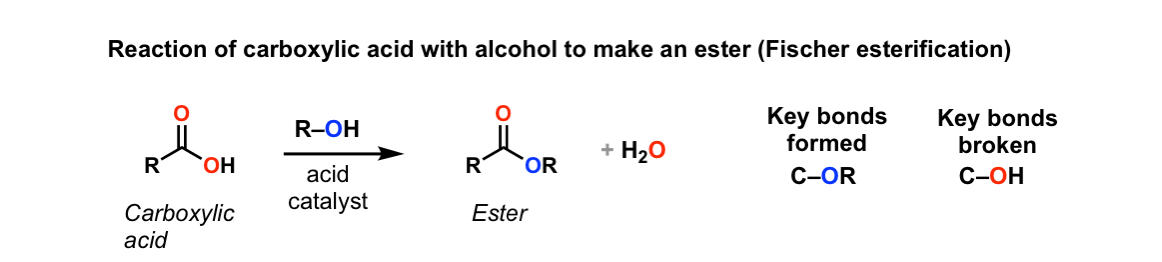

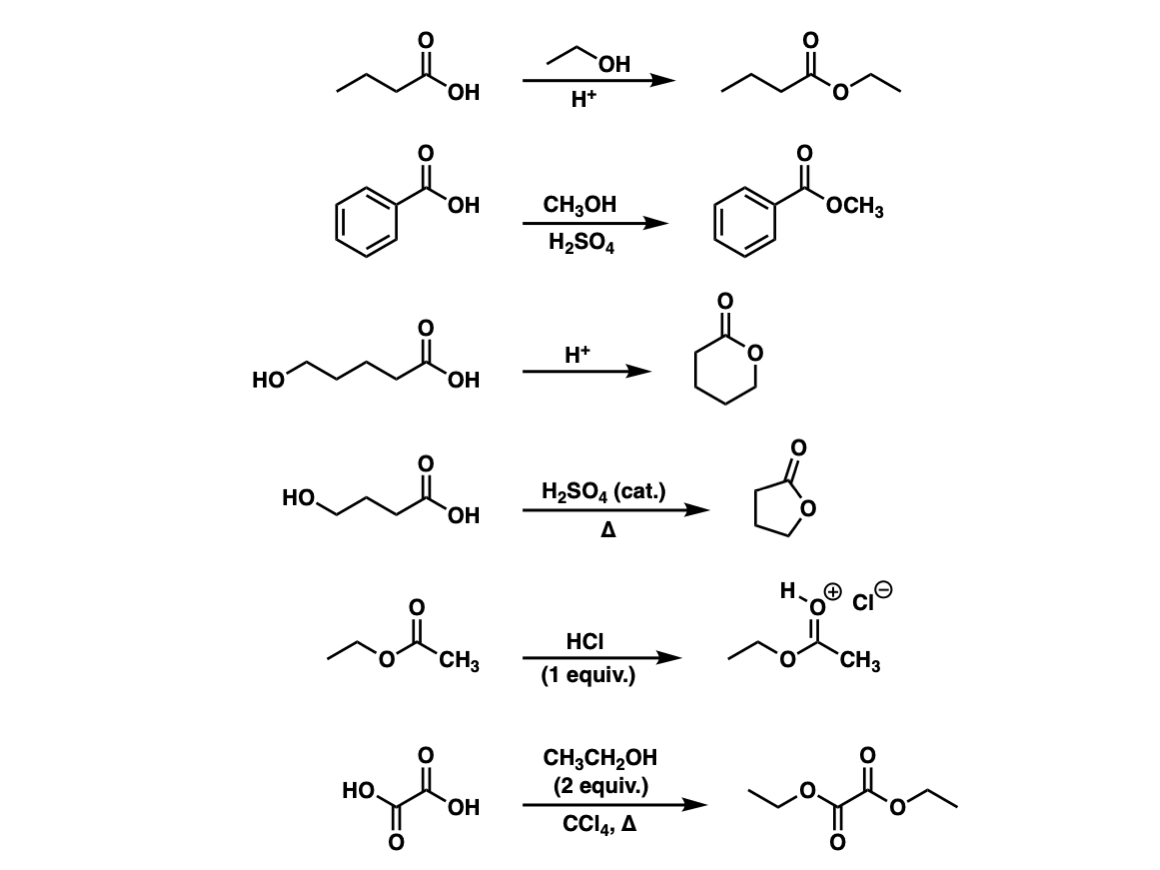

Categories: Details 16 How Can The Fischer Esterification Be Driven To Completion
See more here: muadacsan3mien.com
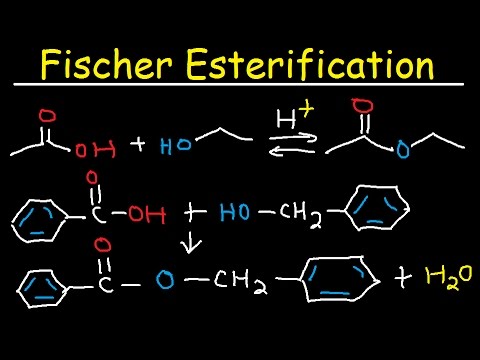
The overall reaction is reversible; to drive the reaction to completion, it is necessary to exploit Le Chateliers principle, which can be done either by continuously removing the water formed from the system or by using a large excess of the alcohol.Esters are made in esterification reactions, which are reversible reactions between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, using a strong acid as a catalyst. Esters can be hydrolysed using an acid or a base. Acid hydrolysis is the reverse of esterification, and as a result doesn’t go to completion.A strong-acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid is required. Even then the reaction is an equilibrium and so does not go to completion. For esters in which the alcohol and carboxylic acid are sterically unhindered, a 1:1 mixture of alcohol and carboxylic acid will yield an equilibrium mixture that is about 70% ester.
Learn more about the topic How can the Fischer esterification be driven to completion.
- Fischer Esterification – Chemistry LibreTexts
- Reactions of Esters – Shiken
- Esters. An Introduction.
- Fischer Esterification
- Fischer Esterification – Kemicalinfo
- Fisher Esterification, Reflux, Isolation and Purification of Esters
See more: blog https://muadacsan3mien.com/category/space-astronomy